Colasoft MAC Scanner will display scan results in the list, including IP address, MAC address, Host Name and Manufacture. It will group all IP addresses according to MAC address if a MAC address is configured with multiple IP addresses. The scanned results can be exported into.txt file for future reference.
Port scanners are some of the most useful tools when you are starting your security investigation on any remote or local network. Let's explore the top five most popular port scanners tools used in the infosec field.
- Jun 27, 2020 Angry IP scanner simply pings each IP address to check if it's alive, then optionally it is resolving its hostname, determines the MAC address, scans ports, etc. You may want to check out more software for Mac, such as IP Scanner Home, IP Scanner Pro or IP Scanner, which might be related to Angry IP Scanner.
- Paid Compredia Mac OS X 10.2/10.3/10.3.9/10.4 Intel/10.4 PPC Version 1.0 Full Specs. Download Now Secure Download. Publisher's Description. From Compredia: Simple Portscanner for OS X.
Used by programmers, system and network administrators, these tools are applications designed to scan servers and hosts in order to check what available ports are being used for network communications.
Once the scan has finished, you can run other security penetration and exploit tests in order to verify how strong are the current security policies. Krita for mac os x 10.10.
Let's explore the top five most popular port scanners tools used in the infosec field.
Wireless Scanner For Mac
1. Nmap
Nmap stands for 'Network Mapper', it is the most popular network discovery and port scanner in the history.
It's a free and open source application used by system administrators, devops and network engineers for security auditing on local and remote networks.
Available for Linux, Windows and Mac OS, it can be run from the classic command line terminal, or by using a GUI interface.
Stay in the loop with the best infosec news, tips and tools
Follow us on Twitter to receive updates!
Nmap features
- Active Port scanning: allows you to scan and discover open ports on specific networks/hosts.
- Host discovery: lets you identify potential hosts that are responding to network requests.
- OS detection: used to discover operating system name and version, along with network details where the host is running.
- Application version detection: nmap can also be used to determine what kind of apps are running and along with the version number.
Installing Nmap
Let's see how Nmap can be installed on the most popular Linux distros, as well as for MacOS users:
Advanced Port Scanner For Mac
CentOS/RHEL based distros:
Ubuntu/Debian users:
For MacOS:
or
Windows users should read these instructions.
Nmap scan examples
Detecting connected devices on the network
For this we will use -sP parameters, this will send ICMP and ARP packets to all possible addresses inside the 192.168.2.0/24 range.
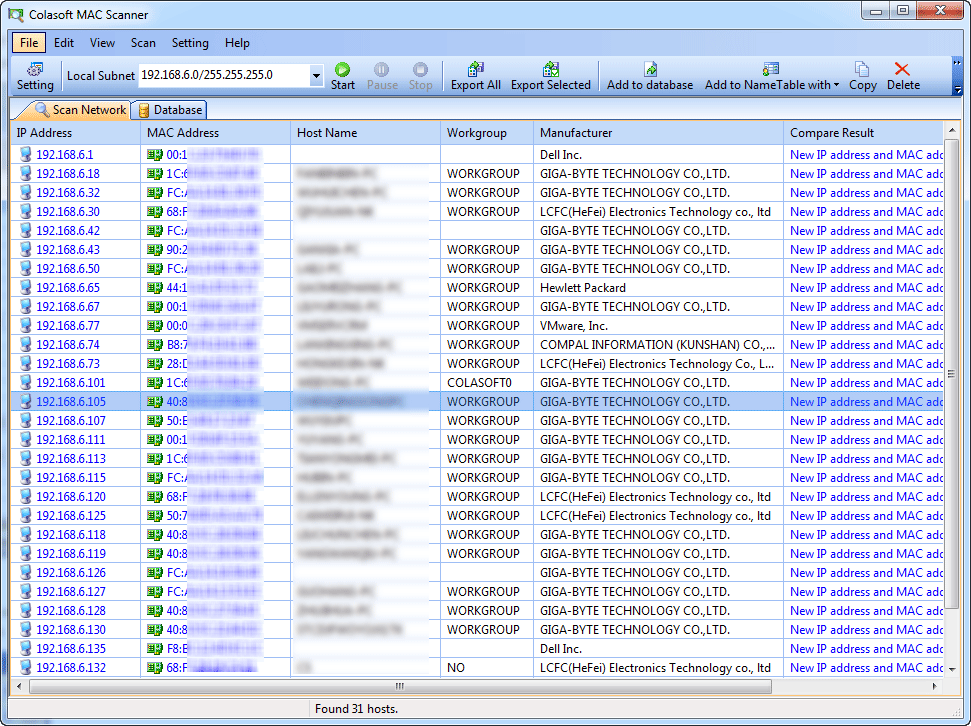
Once finished will show you a resume revealing the devices found in that range.
This simple command will send various packets (ARP, ICMP, etc.) to every address within the 192.168.1.0/24 range, and will report any devices that respond. Is there xsplit for mac. The results will look similar to those in the example below:
Scanning specific ports
Once you have a defined host to scan, you can go against a specific port range (between 1 and 65535), for example:
As you see here, we have ports 21, 80 and 443 open to the public.
This is just a tiny example of how nmap can be used to discover network services and scan remote ports, start reading the official docs https://nmap.org/docs.html to learn more advanced nmap techniques.
2. Unicornscan
Unicornscan is the second most popular free port scanner after Nmap. It's widely known because of its asynchronous TCP and UDP scanning capabilities, along with non-common network discovery patterns that provide alternative ways to explore details about remote operating systems and services.
Unicornscan features
- Asynchronous stateless TCP scanning.
- Asynchronous UDP scanning.
- IP port scanner and service detection.
- Remote operating system detection.
- Enable multiple modules from command-line
Installing Unicornscan
The best suggestion to run Unicornscan is to grab it from the free tools included at Kali Linux distribution, although you can also install it on the most popular Linux distros:
For Ubuntu/Debian users:
Download the source code:
For Fedora users:
Unicornscan scan examples
Let's see what Unicornscan has to offer, for this we will type:
unicornscan --help, and we will get the full list of available options
Mac Network Scanner Free
Unicornscan uses a really simple syntax. Let's try our first basic TCP SYN scan:
Scan multiple hosts:
Now we will scan the entire /24 range, but try to detect which one has telnet open (port 23):
And if you want to send a fake the scan source IP address you just need to add the -s argument, as you see below:
In this case, we scanned the full /24 range that belongs to www.securitytrails.com IP range, and a service detection against 80 port.
Need more unicorn examples? The old beloved man page is always there to help you:
3. Angry IP Scan
Angry IP scanner is our third recommended port scan tool for network discovery. It's popular for its fast scanning speed thanks to its multi-thread approach separating each scan.
It's also free and multiplatform, available for Windows, Mac or Linux operating systems.
Angry IP scanner main features include:
- Download and run, no installation needed.
- Scan for open ports on any remote network.
- Webserver & NetBIOS information detection.
- Export scan results into TXT, XML or CSV files.
- Easy plugin integration with Java language.
Installing Angry IP scanner
Angry IP scanner can be installed on Windows, Linux, and MacOS, all the required packages can be downloaded from the official website.
Ubuntu/Debian:
CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
Angry IP scanner scan examples
Open up a terminal and type ipscan.
From there you will be launching a GUI that will help you to scan hosts from a friendly human interface:
As you see you will be able to specify an IP to scan, or even scan a random IP from the selector at the upper-right corner.
Hit start and let the fun begin. Once completed you will get the full stats including total scan time, average time per host, the number of hosts scanned, and how many are alive.
4. Netcat
Netcat is one of the oldest network tools in the 'Unixverse', it's been there since 1995, and the last official version is from 2004. Although it has many forks and variants that work pretty well on modern operating systems, like ncat from the Nmap suite, or this alternative Netcat version from Mike Frysinger.
While their creators always claimed that Netcat was just a read and write UDP / TCP tool, it can be used for a very wide range of objectives, like open remote connections, tunneling and proxying, run remote commands, as well as port scanning.
Netcat features:
- Built-in port-scanning capabilities.
- TCP and UDP port scan support.
- Verbose port scanning.
- Read command line arguments from standard input.
- Forks available for Windows, Linux, and MacOS.
Installing Netcat
Installing netcat on Ubuntu/Debian:
Installing netcat on CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
Netcat scan examples
Establish a connection to a remote port if open:
As you see, netcat was able to reach 22 port and establish the connection successfully.
UDP port connections are also allowed with netcat, as you can see in the next example:
Netcat also has the ability to open a remote backdoor on the target system for 5000ms, see below:
This will open the backdoor on port 54321 on the local system, then we will have to open a connection to gain system access:
This technique is widely used by penetration testers, and by malicious crackers.
Take a look at ncat --help option if you want to learn more examples about how to use netcat.
5. Zenmap
Zenmap is not a new port scanner, but the official NMAP Front End interface (GUI). For those who are not familiar with command line terminals, Nmap creators launched this GUI release that will allow you to scan remote hosts in a fancy and friendly way.
Zenmap features include:
- Save scan results in a database.
- Search the results database.
- Compare current scan results with previous scans.
- Save port scan profiles for frequently used port discovery options.
Installing Zenmap
Ubuntu/Debian users:
CentOS/RHEL/Fedora users:
Zenmap scan examples
As we told before, Zenmap is just the front end human-friendly interface of Nmap, the classic network mapper that is present on almost every Linux distribution.
Zenmap has a pretty basic interface, that will allow you to run any scans like the command line version of Nmap, as you see in the following screenshot:
In the same way port scanners are useful tools to gather information about any target open ports, SecurityTrails is the perfect tool to integrate with your port scanner results, as it can reveal DNS server information, DNS records data associated with IPs and Domain names, technology used on web apps, as well as WHOIS and even DNS history.
Get a free API account today to unveil the full power of our intelligence cyber-security platform. And if you find anything interesting, remember we also have a cool bug bounty program waiting for you!

Once finished will show you a resume revealing the devices found in that range.
This simple command will send various packets (ARP, ICMP, etc.) to every address within the 192.168.1.0/24 range, and will report any devices that respond. Is there xsplit for mac. The results will look similar to those in the example below:
Scanning specific ports
Once you have a defined host to scan, you can go against a specific port range (between 1 and 65535), for example:
As you see here, we have ports 21, 80 and 443 open to the public.
This is just a tiny example of how nmap can be used to discover network services and scan remote ports, start reading the official docs https://nmap.org/docs.html to learn more advanced nmap techniques.
2. Unicornscan
Unicornscan is the second most popular free port scanner after Nmap. It's widely known because of its asynchronous TCP and UDP scanning capabilities, along with non-common network discovery patterns that provide alternative ways to explore details about remote operating systems and services.
Unicornscan features
- Asynchronous stateless TCP scanning.
- Asynchronous UDP scanning.
- IP port scanner and service detection.
- Remote operating system detection.
- Enable multiple modules from command-line
Installing Unicornscan
The best suggestion to run Unicornscan is to grab it from the free tools included at Kali Linux distribution, although you can also install it on the most popular Linux distros:
For Ubuntu/Debian users:
Download the source code:
For Fedora users:
Unicornscan scan examples
Let's see what Unicornscan has to offer, for this we will type:
unicornscan --help, and we will get the full list of available options
Mac Network Scanner Free
Unicornscan uses a really simple syntax. Let's try our first basic TCP SYN scan:
Scan multiple hosts:
Now we will scan the entire /24 range, but try to detect which one has telnet open (port 23):
And if you want to send a fake the scan source IP address you just need to add the -s argument, as you see below:
In this case, we scanned the full /24 range that belongs to www.securitytrails.com IP range, and a service detection against 80 port.
Need more unicorn examples? The old beloved man page is always there to help you:
3. Angry IP Scan
Angry IP scanner is our third recommended port scan tool for network discovery. It's popular for its fast scanning speed thanks to its multi-thread approach separating each scan.
It's also free and multiplatform, available for Windows, Mac or Linux operating systems.
Angry IP scanner main features include:
- Download and run, no installation needed.
- Scan for open ports on any remote network.
- Webserver & NetBIOS information detection.
- Export scan results into TXT, XML or CSV files.
- Easy plugin integration with Java language.
Installing Angry IP scanner
Angry IP scanner can be installed on Windows, Linux, and MacOS, all the required packages can be downloaded from the official website.
Ubuntu/Debian:
CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
Angry IP scanner scan examples
Open up a terminal and type ipscan.
From there you will be launching a GUI that will help you to scan hosts from a friendly human interface:
As you see you will be able to specify an IP to scan, or even scan a random IP from the selector at the upper-right corner.
Hit start and let the fun begin. Once completed you will get the full stats including total scan time, average time per host, the number of hosts scanned, and how many are alive.
4. Netcat
Netcat is one of the oldest network tools in the 'Unixverse', it's been there since 1995, and the last official version is from 2004. Although it has many forks and variants that work pretty well on modern operating systems, like ncat from the Nmap suite, or this alternative Netcat version from Mike Frysinger.
While their creators always claimed that Netcat was just a read and write UDP / TCP tool, it can be used for a very wide range of objectives, like open remote connections, tunneling and proxying, run remote commands, as well as port scanning.
Netcat features:
- Built-in port-scanning capabilities.
- TCP and UDP port scan support.
- Verbose port scanning.
- Read command line arguments from standard input.
- Forks available for Windows, Linux, and MacOS.
Installing Netcat
Installing netcat on Ubuntu/Debian:
Installing netcat on CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
Netcat scan examples
Establish a connection to a remote port if open:
As you see, netcat was able to reach 22 port and establish the connection successfully.
UDP port connections are also allowed with netcat, as you can see in the next example:
Netcat also has the ability to open a remote backdoor on the target system for 5000ms, see below:
This will open the backdoor on port 54321 on the local system, then we will have to open a connection to gain system access:
This technique is widely used by penetration testers, and by malicious crackers.
Take a look at ncat --help option if you want to learn more examples about how to use netcat.
5. Zenmap
Zenmap is not a new port scanner, but the official NMAP Front End interface (GUI). For those who are not familiar with command line terminals, Nmap creators launched this GUI release that will allow you to scan remote hosts in a fancy and friendly way.
Zenmap features include:
- Save scan results in a database.
- Search the results database.
- Compare current scan results with previous scans.
- Save port scan profiles for frequently used port discovery options.
Installing Zenmap
Ubuntu/Debian users:
CentOS/RHEL/Fedora users:
Zenmap scan examples
As we told before, Zenmap is just the front end human-friendly interface of Nmap, the classic network mapper that is present on almost every Linux distribution.
Zenmap has a pretty basic interface, that will allow you to run any scans like the command line version of Nmap, as you see in the following screenshot:
In the same way port scanners are useful tools to gather information about any target open ports, SecurityTrails is the perfect tool to integrate with your port scanner results, as it can reveal DNS server information, DNS records data associated with IPs and Domain names, technology used on web apps, as well as WHOIS and even DNS history.
Get a free API account today to unveil the full power of our intelligence cyber-security platform. And if you find anything interesting, remember we also have a cool bug bounty program waiting for you!
Esteban is a seasoned security researcher and cybersecurity specialist with over 15 years of experience. Since joining SecurityTrails in 2017 he's been our go-to for technical server security and source intelligence info.
